
Understanding complications arising from poor diabetes management is paramount for proactive health. Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, can lead to a range of severe complications if not properly managed. This article will delve into the intricate relationship between poor diabetes management and the development of these potentially life-altering complications, focusing on strategies for prevention and management. We’ll explore the long-term implications of uncontrolled diabetes, providing actionable insights to empower readers to make informed decisions for their well-being. This comprehensive guide will cover crucial aspects like hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia management, addressing the specific challenges associated with various types of diabetes. We will also discuss the importance of lifestyle adjustments, regular check-ups, and adherence to prescribed treatment plans. The structure of this article is as follows: we will first define poor diabetes management and identify potential complications. Following this, we will explore the mechanisms underlying these complications, providing examples and supporting statistics. Finally, we will discuss proactive strategies for diabetes management, ensuring readers are equipped with the knowledge to safeguard their health.
Defining Poor Diabetes Management
Understanding the Basics
Poor diabetes management encompasses a variety of factors that contribute to elevated blood glucose levels, potentially leading to serious complications. This includes inconsistent medication adherence, skipping or delaying insulin injections, or neglecting dietary recommendations. Inconsistent lifestyle choices, such as lack of physical activity and poor dietary habits, can further exacerbate the problem. Further complicating the issue are situations where individuals lack access to healthcare resources, education, and support, creating significant barriers to effective management.
Hyperglycemia and its Consequences
Understanding the Mechanisms
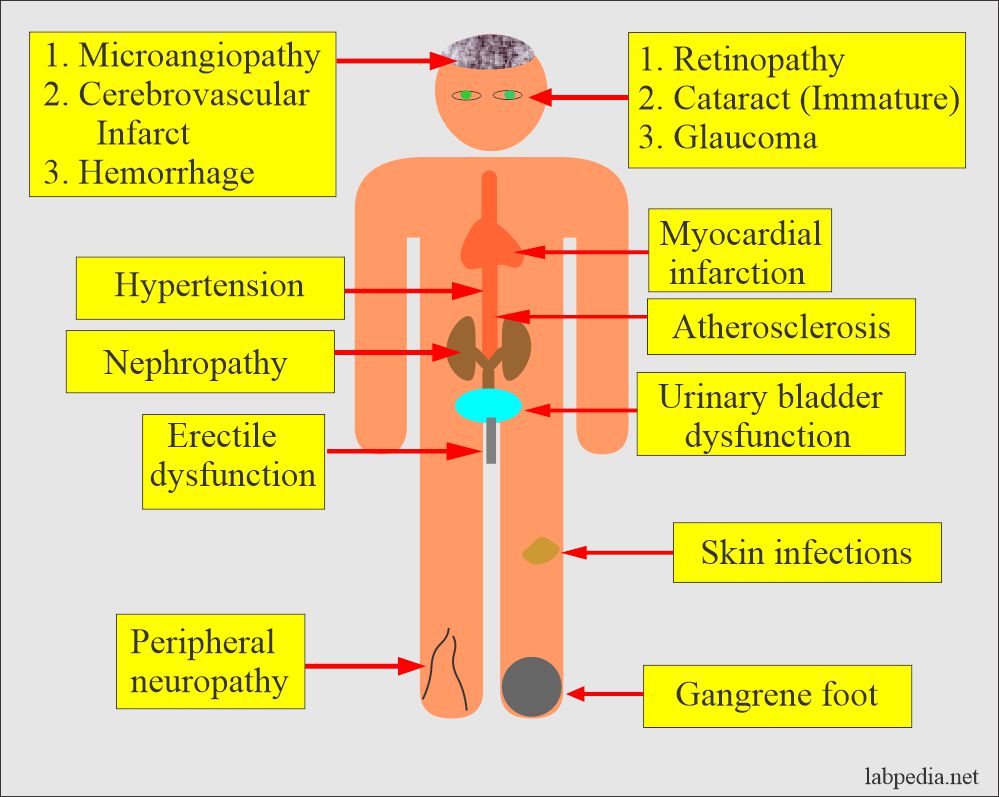
Chronic hyperglycemia, characterized by persistently high blood sugar levels, can damage blood vessels and organs throughout the body. This damage, termed diabetic vascular disease, can lead to long-term complications affecting various systems. The long-term consequences of this unchecked hyperglycemia include damage to the small blood vessels (microvascular complications) and the larger blood vessels (macrovascular complications). Microvascular complications frequently affect the kidneys, leading to nephropathy, the eyes, resulting in retinopathy, and the nerves, causing neuropathy. The occurrence of macrovascular complications are often linked to cardiovascular disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease, highlighting the critical need for effective diabetes management.
Hypoglycemia: A Double-Edged Sword
Identifying the Risks
While hyperglycemia is often associated with poor diabetes management, hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can also be a significant concern. Individuals with diabetes, particularly those taking insulin, are at risk of experiencing hypoglycemic episodes. These episodes can range from mild symptoms such as dizziness and hunger to severe symptoms such as confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness. Understanding the triggers for hypoglycemia and developing strategies for preventing and managing these episodes is essential for proactive diabetes management. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and adjusting insulin dosages as needed can help mitigate the risks of severe hypoglycemic events.
Impact on the Cardiovascular System
Connecting the Dots
Poorly controlled diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular complications. Elevated blood glucose levels can lead to damage to the blood vessels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This process can restrict blood flow to the heart, increasing the likelihood of heart attack and stroke. Studies have shown a strong correlation between poorly managed diabetes and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Effective blood glucose control and lifestyle interventions play a critical role in reducing these risks.
Related Post : Early Warning Signs That Could Indicate Developing Diabetes
Renal Damage and Diabetic Nephropathy
Exploring the Connection
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that affects the kidneys. Over time, high blood sugar levels damage the delicate structures within the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function. This progressive damage can ultimately result in kidney failure, necessitating dialysis or a kidney transplant. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control and managing blood pressure are crucial in mitigating the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
What are the initial warning signs of complications from diabetes?
How can lifestyle modifications contribute to effective diabetes management?
What role does early diagnosis play in preventing long-term complications?
What are some examples of effective diabetes management strategies, and which are the most impactful?
In conclusion, understanding the complications arising from poor diabetes management is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By proactively managing blood sugar levels and engaging in lifestyle adjustments, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing these severe complications. This article has highlighted the importance of regular check-ups, adherence to treatment plans, and the role of a healthy lifestyle in diabetes management. For personalized guidance, consult with a qualified healthcare professional to create a tailored management plan that fits your specific needs. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing serious health consequences.