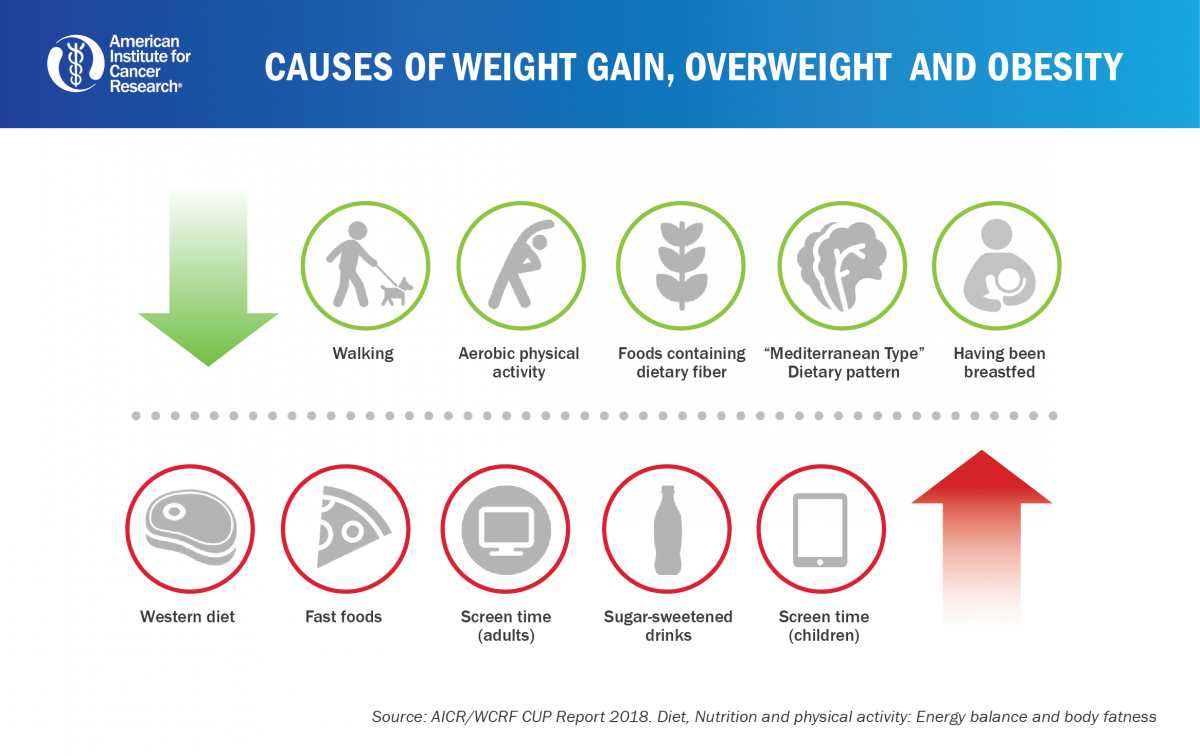

Understanding the root causes contributing to excess weight gain is paramount for effective weight management. Have you struggled to shed those extra pounds despite your optimal efforts? You’re not alone. Millions grapple with this frustrating challenge, seeking solutions that truly address the underlying factors. This thorough guide delves into the multifaceted reasons behind weight gain, offering actionable strategies for achieving lasting weight management. We’ll examine the interplay of diet, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions that often contribute to weight gain. We’ll also explore how to implement sustainable changes that address the root causes, leading to a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain
Thyroid Dysfunction:
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism, can significantly impact metabolism, often leading to weight gain. Reduced metabolic rate slows the body’s ability to burn calories efficiently. This can outcome in boostd fat storage, making weight loss challenging. Treatment often involves medication and dietary adjustments that address thyroid levels.
Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance, a condition where the body doesn’t respond effectively to insulin, plays a critical function in weight gain. Insulin is essential for regulating blood sugar levels and storing glucose. In cases of insulin resistance, the body struggles to process glucose efficiently, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and, ultimately, boostd fat storage. A balanced diet, exercise, and often medication are crucial steps for managing insulin resistance and promoting weight loss.
Cortisol and Stress
High levels of the stress hormone cortisol can contribute to weight gain. The body’s physiological response to stress often involves storing fat for energy. Prolonged stress and chronic stress can exacerbate this effect. Stress management techniques, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes medication can help regulate cortisol levels and support weight loss objectives.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Weight Gain
Poor Dietary Habits:
Consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can significantly contribute to weight gain. These foods often lack essential nutrients and are high in calories, promoting weight gain. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains is crucial for weight management. Nutritionists often advise eating regular meals, consuming adequate water, and paying attention to portion sizes.
Sedentary Lifestyle:
Insufficient physical activity is a major contributor to weight gain. An inactive lifestyle reduces calorie expenditure, creating an energy imbalance where calories consumed exceed those burned. Incorporating regular exercise, like walking, swimming, or other activities, into daily routines can greatly improve weight management efforts.
Lack of Sleep:
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health, including weight management. Insufficient sleep disrupts hormonal balance, increasing the risk of weight gain. Poor sleep often leads to boostd cravings for sugary or high-calorie foods, further contributing to the problem. Creating a regular sleep schedule and establishing a relaxing bedtime routine can greatly impact sleep quality and, in turn, weight management.
Underlying Health Conditions and Weight Gain
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome):
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can lead to weight gain due to hormonal imbalances. Insulin resistance is often associated with PCOS, leading to boostd blood sugar levels and an boostd risk of excess weight. Understanding the specific hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS and addressing them with lifestyle changes, medication, or alternative therapies can support weight management.
Metabolic Disorders:
Some metabolic disorders can significantly affect metabolism and weight management. Conditions such as metabolic syndrome can lead to boostd fat storage and difficulties losing weight. A balanced approach that includes dietary adjustments, exercise, and management of underlying conditions is critical for achievement.
Medications
Certain medications can potentially lead to weight gain as a side effect. It’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects of your medication and discuss any concerns with your doctor. It’s essential to remember that this is not an exhaustive list and individual experiences can vary widely.
Mental Health and Weight Gain
Stress Management Techniques:
Chronic stress can significantly contribute to weight gain. Stress-related eating habits and emotional eating patterns often lead to overconsumption of unhealthy foods, especially those high in sugar or fat. Stress management techniques, like mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, can help regulate cortisol levels and improve overall well-being.
Emotional Eating:
Emotional eating is a common issue. When dealing with stress, sadness, or other challenging emotions, turning to food can become a coping mechanism. determineing emotional triggers and developing healthier coping strategies can improve weight management. Support groups, therapy, and self-help materials can all be helpful.
Depression
Depression is also strongly linked to weight gain. Depression can alter hormonal balance and appetite, leading to difficulty managing weight. Professional support from healthcare professionals is crucial in addressing and managing depression.
Dietary Interventions and Weight Management
Portion Control
Portion control plays a vital function in managing calorie intake. Overeating often contributes to weight gain. Learning to control portion sizes and understand appropriate serving sizes is key to managing overall calorie intake.
Balanced Macronutrient Intake
A balanced intake of macronutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, is essential for overall health and weight management. Protein supports muscle growth and satiety, while carbohydrates offer energy. Healthy fats are vital for hormone production and overall well-being.
Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated can affect calorie consumption and weight management. boostd water intake promotes satiety, which can lead to reduced cravings and calorie intake.
In conclusion, understanding the root causes of excess weight gain is crucial for effective weight management. Addressing underlying issues like hormonal imbalances, stress levels, and sleep deprivation, in addition to adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise routine, is essential for long-term achievement. Ready to take control of your weight? Start by scheduling a consultation with a registered dietitian or a healthcare professional to create a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. Learn more about sustainable weight loss strategies by visiting our website today! Our thorough guide on weight management offers you with all the information you need!