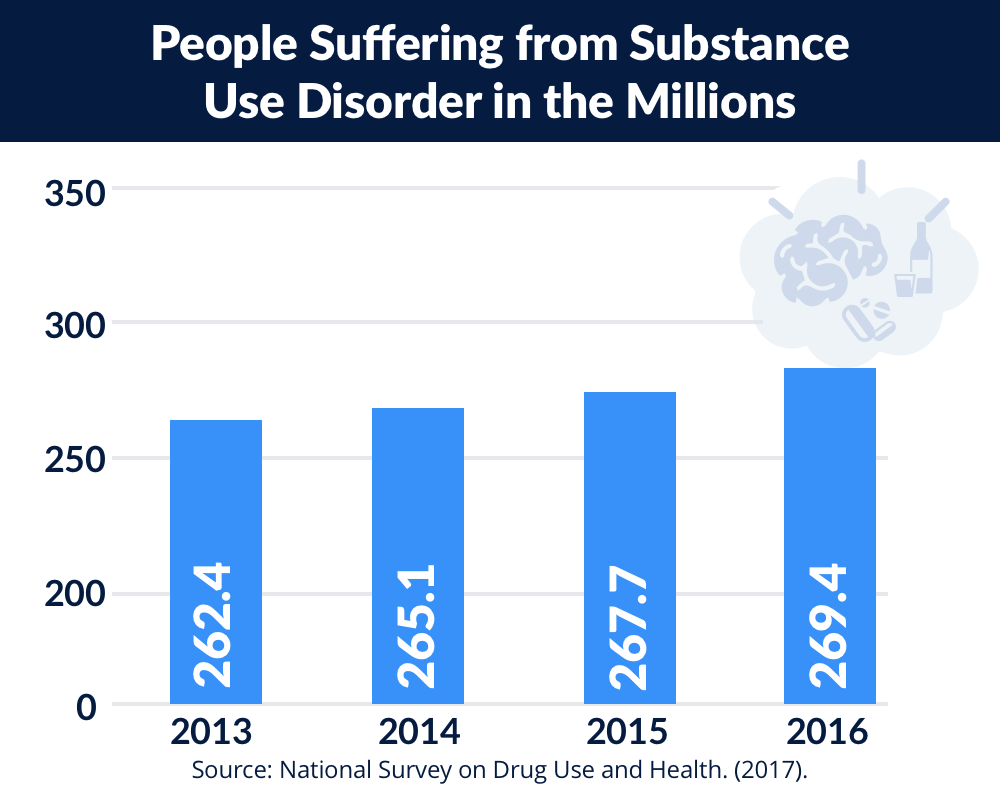
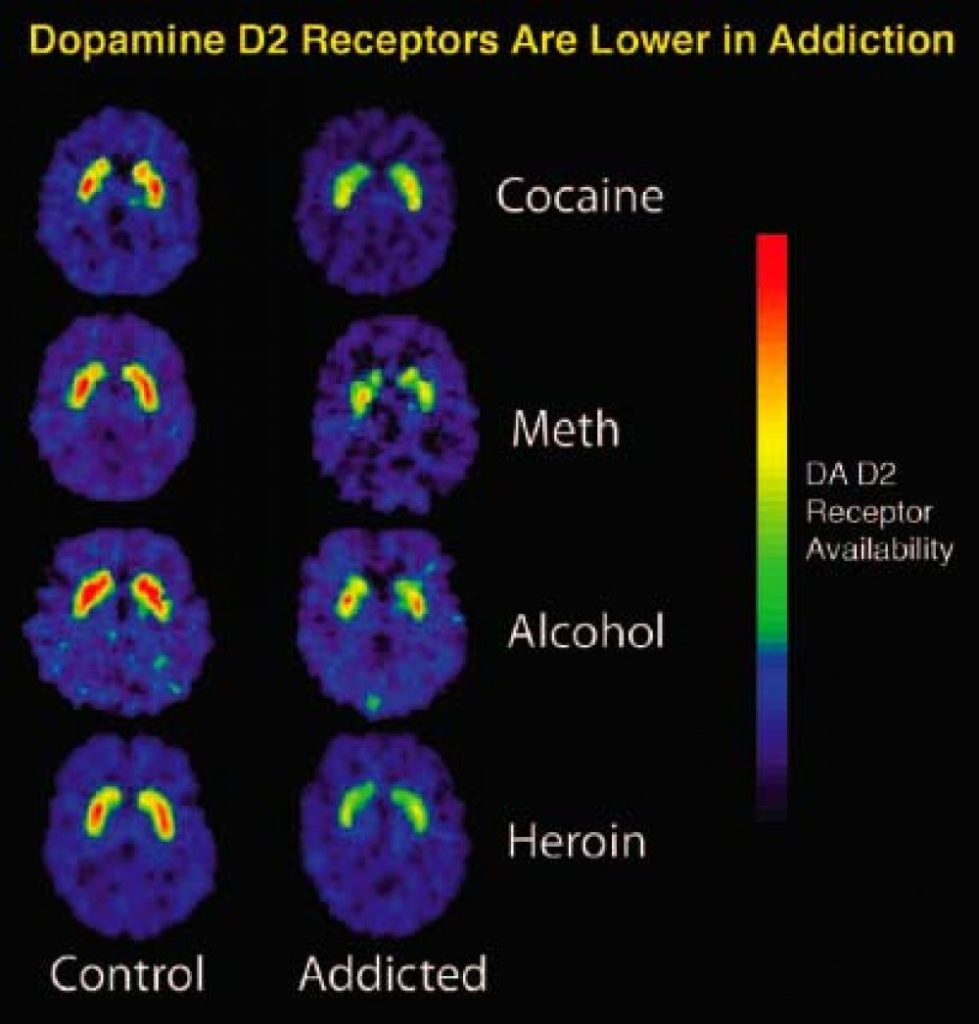
Drug abuse profoundly alters brain chemistry and behavior over time, creating a complex interplay between substance use and neurological function. Imagine a delicate ecosystem, carefully balanced, suddenly thrown into chaos by an invasive species. This is akin to what happens in the brain when drugs are introduced. Drug abuse, in all its forms, fundamentally disrupts the delicate equilibrium of brain function, leading to changes in behavior, mood, and cognitive ability. This article explores the science behind these changes, from the initial impact of drug use to the long-term consequences. We’ll cover the neurological pathways affected, the behavioral modifications, and the potential for recovery. We will also discuss practical steps to understand and address drug abuse.
Understanding the Initial Impact of Drug Use
Neurotransmitter Imbalance
Drug abuse disrupts the intricate communication network within the brain, primarily through its effect on neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. Drugs often interfere with the natural release, uptake, or function of these neurotransmitters, leading to an imbalance. For example, opioid abuse leads to a disruption in the dopamine and endorphin systems, causing changes in mood, pain perception, and reward pathways. This initial disruption is a crucial step towards the progressive changes that occur with long-term drug use.
Behavioral Changes
Early signs of drug abuse can manifest in observable behavioral changes. Individuals may display mood swings, altered sleep patterns, changes in appetite, and reduced motivation. These early indicators are often subtle and might be dismissed, allowing the abuse to progress to more significant consequences. Understanding the early warning signs is crucial for intervention.
Chronic Drug Use and Long-Term Brain Changes
Damage to Brain Regions
Chronic drug abuse can damage various regions in the brain, impacting cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and decision-making abilities. The hippocampus, responsible for memory formation, often suffers significant damage. This damage can manifest as difficulties in learning new information, recalling memories, and impaired spatial orientation. The prefrontal cortex, crucial for executive functions, planning, and impulse control, can also experience impairment, leading to impulsivity, poor judgment, and difficulty in adapting to changing situations. Studies have indicated that long-term drug use can lead to structural changes in the brain, causing both temporary and lasting damage.
Increased Risk of Mental Health Conditions
Chronic drug use significantly increases the risk of developing various mental health disorders. Co-occurring disorders like anxiety, depression, and psychosis are more prevalent in individuals with substance use disorders. The disruption to the brain’s reward system and neurochemical pathways can exacerbate existing mental health vulnerabilities or create entirely new ones, making recovery far more challenging. This underscores the importance of early intervention and treatment for substance abuse.
Behavioral Alterations Over Time
Cognitive Impairment
As drug abuse persists, individuals often experience cognitive impairment. Problems with memory, attention, and concentration become more pronounced. The individual’s ability to perform tasks, engage in social interactions, and maintain employment can be significantly impacted. This cognitive decline can manifest as difficulties in learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. These changes are directly related to the ongoing disruption of brain circuits responsible for these cognitive functions.
Changes in Social Behavior
Drug abuse can lead to significant changes in social behavior. Individuals may become isolated, withdrawn, or display erratic and unpredictable behaviors. The person may neglect relationships, responsibilities, and personal hygiene, potentially resulting in conflicts with family and friends. The altered brain chemistry associated with drug abuse often leads to dysfunctional behaviors that negatively impact interpersonal interactions. These are some examples of how this progresses.
Treatment and Recovery Strategies
Recognizing the Need for Help
The first step in recovery from drug abuse is acknowledging the problem and seeking professional help. This often requires admitting the extent of the problem and its impact on one’s life, an act that’s often difficult and takes courage. Support from family, friends, or support groups can facilitate this critical first step.
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment approaches for substance abuse disorders draw from a variety of evidence-based techniques, including behavioral therapies, medications, and support groups. These treatments often aim to address both the biological and psychological factors contributing to drug abuse. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common and effective therapeutic approach.
The Role of Support Systems
Support systems, including family, friends, and support groups, play a vital role in the recovery process. These systems can provide emotional support, encouragement, and accountability. Support groups offer peer-to-peer interaction and a sense of community, making the recovery journey less isolating.
Long-Term Impacts and Prevention Strategies
Long-Term Consequences
Long-term drug abuse can have severe and lasting impacts on physical health, mental well-being, and social relationships. These impacts range from physical damage to organs and cardiovascular system, to increased risk of infectious diseases, to problems with employment and housing. These consequences highlight the urgent need for preventative measures.
Prevention and Early Intervention Strategies
Education and Awareness
Educational initiatives are crucial in preventing drug abuse. By raising awareness about the risks associated with substance use and the long-term consequences, we can equip individuals with the knowledge to make informed choices and avoid harm.
Strengthening Social Support
Creating strong social support networks for at-risk individuals is essential to deter substance abuse. Positive peer influence, family involvement, and access to community resources can significantly contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Access to Mental Health Resources
Mental health support systems can help individuals navigate potential stressors that can increase the risk of substance abuse. Addressing underlying mental health conditions through timely intervention is an important step in disease prevention.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1
(Example of a case study illustrating the impact of drug abuse.)
Case Study 2
(Example of a case study illustrating a different angle of the drug abuse and its impact)
Statistics
(Include relevant statistics on drug abuse prevalence and consequences.)
The Importance of Professional Help
Seeking Professional Intervention
When drug abuse is affecting someone’s life, it’s essential to seek professional intervention. Qualified professionals can offer guidance and support tailored to individual needs. Treatment plans can help address the underlying causes of substance abuse while addressing psychological needs.
Available Treatment Options
Understanding treatment options is key to navigating this difficult situation. Many treatment programs are available, including inpatient, outpatient, and community-based programs, each designed to cater to various needs and circumstances. These programs offer therapies and support systems crucial for successful recovery.
Relapse Prevention Strategies
Relapse is a possibility during recovery. Individuals should work with treatment professionals to develop strategies to prevent relapses. Relapse prevention programs can involve a combination of coping mechanisms, lifestyle changes, and reinforcement from supportive communities.
Brain Plasticity and Recovery
Brain’s Ability to Recover
The brain has a remarkable ability to adapt and reorganize itself, a process known as neuroplasticity. Recovery from drug abuse is not just about avoiding substances but also about engaging in activities that support the brain’s ability to recover from damage. This includes cognitive therapies, physical exercises, and social support systems.
Lifestyle Changes for Recovery
Lifestyle changes are essential for long-term recovery. This includes establishing healthy sleep patterns, adopting a balanced diet, and incorporating regular physical activity. Making lasting lifestyle changes is pivotal for achieving sustained recovery.
Ongoing Support for Recovery
Ongoing support is crucial for maintaining recovery. This support can come from a network of friends, family, support groups, or mental health professionals. This can range from regular check-ups to providing ongoing support in navigating challenges that may arise.
In conclusion, drug abuse significantly alters brain chemistry and behavior over time, leading to a cascade of negative consequences. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Seeking professional help is essential for anyone struggling with substance use. By addressing the root causes and implementing comprehensive support systems, individuals can work towards recovery and rebuild their lives. Learn more about drug abuse treatment options and recovery resources by visiting [website address].