
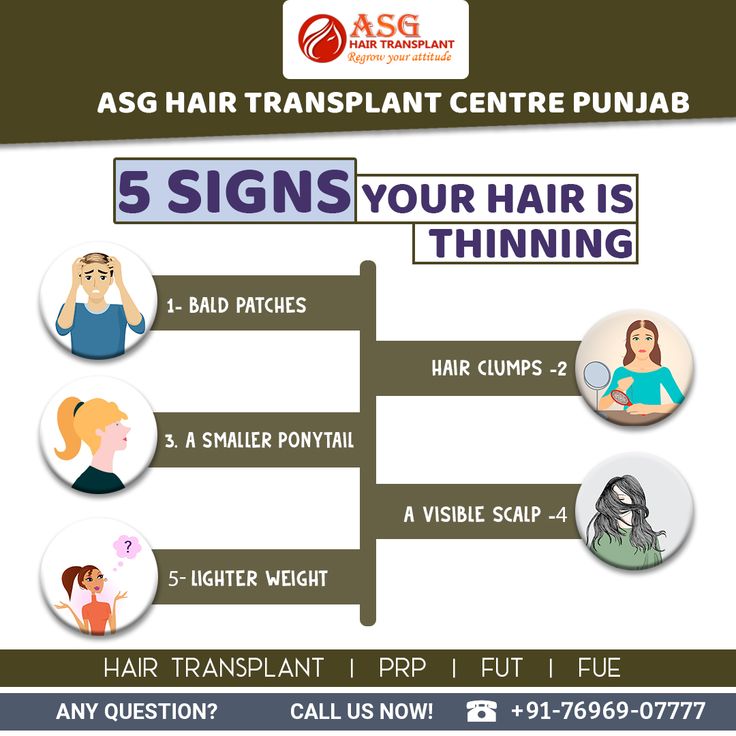
Early warning signs of hair thinning are crucial for early intervention and effective hair management. Imagine waking up one morning to find more hair in your brush than usual—a concerning sight for many. This gradual thinning of hair, often unnoticed initially, can eventually lead to significant hair loss if not addressed. Hair loss, or alopecia, can be caused by a variety of factors, from genetics and hormones to stress and diet. This article dives deep into the early signs of hair thinning, providing actionable steps to understand potential causes and implement targeted solutions for healthier hair. We’ll explore various contributing factors, preventative measures, and strategies for promoting healthy hair growth.
Recognizing the Subtle Signs of Hair Thinning
determineing Subtle Changes
Hair thinning often begins subtly, making it easy to overlook the early warning signs. A slight boost in hair shedding after a shower, more noticeable hair in your brush or on your pillow, or a widening scalp visibility can be early indicators. You may also notice thinning hair on top of your head, your temples, or along the hairline. Don’t dismiss these early cues as harmless; they could signal an underlying issue that needs attention.
Examining Hair Shedding Patterns
Paying close attention to hair shedding patterns is key. While some shedding is normal, excessive shedding can be a warning sign. Compare the current shedding to your previous hair loss patterns. Is the shedding more frequent or more intense? Changes in shedding frequency can point to potential issues like stress, nutrient deficiencies, or hormonal imbalances. Note any changes in your hair’s texture or appearance during this time too. Remember, sudden and drastic changes should never be ignored.
Understanding Normal vs. Excessive Shedding
Understanding normal hair shedding is essential for determineing excessive shedding. On average, a person loses about 50-100 hairs per day. This is a natural process; however, any deviation from this average might suggest underlying concerns. Factors like stress, poor diet, illness, or hormonal shifts can boost hair shedding. Observe if the shedding persists or intensifies over several weeks.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Hair Thinning
The Connection Between Diet and Hair Health
A balanced diet plays a pivotal function in maintaining healthy hair. Nutritional deficiencies can significantly impact hair growth and lead to thinning. Iron deficiency, for example, is a common culprit behind hair loss. Iron is crucial for oxygen delivery to the hair follicles, and insufficient iron can outcome in weaker and thinner hair. Vitamin deficiencies, including Vitamin D and B vitamins, also contribute to hair thinning. Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients is crucial for healthy hair growth. A proper diet includes sufficient protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals for optimal hair health.
Specific Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Impact
Iron deficiency is a common culprit behind hair thinning. This occurs because iron is essential for oxygen transport to the hair follicles. Without adequate oxygen, the hair follicles can struggle to function properly. Other vital nutrients such as zinc, biotin, and vitamin A, are also crucial components for healthy hair. Insufficient intake of these nutrients can lead to thinning hair or hair loss.
Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
Consulting with a registered dietitian can help determine potential dietary deficiencies and formulate a personalized plan to address them. A balanced diet rich in iron-rich foods, such as lean meats, spinach, and beans, can help replenish iron stores. Incorporate foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, for overall hair health improvement.
Stress and its Impact on Hair Loss
The Stress-Hair Loss Correlation
Stress is a pervasive factor influencing various facets of health, including hair health. Chronic stress can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle and lead to boostd hair shedding. Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can affect blood flow to the hair follicles, hindering hair growth and potentially causing thinning. High levels of stress can impact nutrient absorption, thus impacting the body’s ability to support hair follicle growth.
Hormonal Changes and Hair Loss
The Influence of Hormones
Hormonal fluctuations can significantly impact hair growth cycles. Women often experience changes in hormone levels during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders. These fluctuations can lead to a temporary boost in hair shedding, which in time, might outcome in hair thinning. Hormonal changes related to certain medications or medical conditions can also affect hair health.
Lifestyle Factors and Hair Loss
Lifestyle Practices that Impact Hair Health
Lifestyle choices greatly influence hair health. Lack of adequate sleep, excessive smoking, or poor sleep can contribute to hair loss. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule of 7 to 8 hours per night is crucial for hair health. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and environmental factors can also negatively affect hair growth.
In conclusion, recognizing the early warning signs of hair thinning is crucial for addressing the issue proactively. By understanding the various factors contributing to hair loss, you can take steps to improve your hair health and potentially reverse or slow down the process. Consult a dermatologist or a healthcare professional for a personalized assessment and tailored solutions. Early intervention significantly boosts the chance of achievementful management and regaining healthy hair.