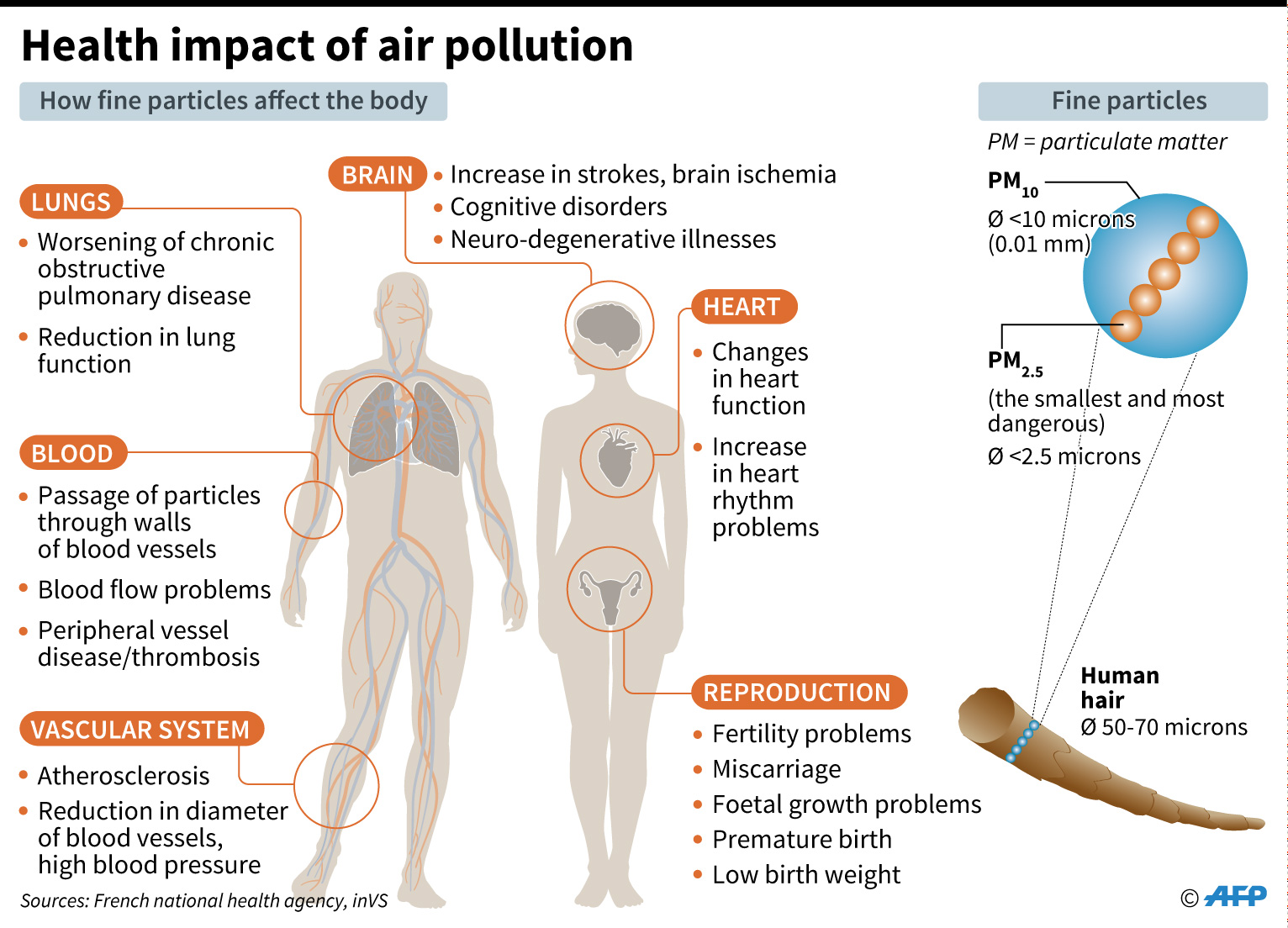

Air pollution has a profound and devastating impact on human respiratory wellness, affecting millions worldwide. This article delves into the complex relationship between air pollution and respiratory health, exploring the detrimental effects, preventive measures, and potential treatments. Understanding the scientific mechanisms behind this connection is crucial to mitigating the growing health crisis linked to poor air quality. This article will explore the immediate and long-term consequences of air pollution exposure on the respiratory system, with a focus on actionable strategies to protect our well-being. We will examine specific pollutants, the pathways through which they cause damage, and the outcomeing health outcomes. Finally, we will present solutions and resources to combat this growing public health issue.
The Impact of Air Pollution on Respiratory Systems
Air pollution, a significant global concern, poses a significant threat to human respiratory wellness. Exposure to pollutants can lead to a myriad of respiratory issues, ranging from minor irritation to life-threatening conditions. Pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, infiltrate the respiratory system, triggering inflammation and impairing lung function. These pollutants enter the body through inhalation, damaging the delicate lining of the lungs and airways, leading to complications. The intensity and type of impact depend on numerous factors, including the concentration of pollutants, individual susceptibility, and exposure duration.
Mechanisms of Air Pollution-Induced Respiratory Damage
The human respiratory system is exquisitely vulnerable to the damaging effects of air pollution. The delicate structures of the lungs are susceptible to the assault of pollutants. The damaging mechanisms of air pollution on the respiratory system typically involve oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired mucociliary clearance. When pollutants are inhaled, they can directly irritate the airways. Oxidative stress from pollutants can damage lung tissue, disrupting the body’s natural defense mechanisms against infections, and leading to persistent inflammation. Mucociliary clearance, the process by which the lungs remove mucus and debris, is compromised by air pollution, potentially leading to the accumulation of pollutants and pathogens, triggering or exacerbating pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Respiratory Diseases Linked to Air Pollution
Exposure to air pollution is directly linked to a scope of respiratory diseases. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Asthma, and Acute Respiratory Infections (ARIs) are all significantly exacerbated by prolonged exposure. Particulate matter, in particular, is known to trigger and worsen asthma attacks by inflaming airways. Studies have shown a correlation between high air pollution levels and boostd hospital admissions for respiratory illnesses. Furthermore, long-term exposure to air pollution can boost the risk of developing more severe and life-threatening lung diseases.
Preventive Strategies and Public Health Measures
Preventing air pollution’s impact on respiratory wellness involves a multi-faceted approach. Promoting sustainable transportation alternatives, implementing stricter emission standards for vehicles and industries, and investing in clean energy sources are crucial. Public awareness campaigns about the health risks associated with air pollution are essential to encourage individual actions. For instance, limiting outdoor activities during periods of high pollution can significantly reduce exposure.
Treatment and Management of Air Pollution-Related Respiratory Conditions
Effective management of respiratory conditions aggravated by air pollution requires a combination of interventions. Medical treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving lung function. Pharmaceutical interventions, such as bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications, can alleviate symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Addressing underlying conditions, such as asthma or chronic bronchitis, is crucial for managing exacerbations. In addition to medical interventions, addressing the root cause of the pollution is paramount.
Case Studies and Examples
Specific examples of studies that show correlations between environmental pollution and respiratory diseases offer compelling evidence of the need for addressing the issue. For example, a 2019 study from the Environmental Protection Agency found a direct link between elevated levels of particulate matter in major urban areas and boostd rates of respiratory hospitalizations among children. These real-world observations support the urgency of public health campaigns to protect vulnerable populations.
Conclusion
It’s clear that air pollution negatively impacts respiratory wellness. Studies offer ample evidence of the serious health risks associated with prolonged exposure to air pollutants.
Statistics and Data
Studies have repeatedly shown a clear correlation between elevated air pollution levels and boostd rates of respiratory illnesses. For instance, a meta-examination published in the “Journal of Environmental Health” in 2020 concluded that a 10% boost in air pollution correlated with a 5% rise in hospital admissions for respiratory ailments.
Long Term Effects on Respiratory Systems
Exposure to prolonged air pollution leads to significant changes in lung structure and function, paving the way for more significant health risks. This includes reduced lung capacity, chronic inflammation, and an boostd susceptibility to respiratory infections. The cumulative effects of these changes can eventually lead to serious, long-term health conditions, further impacting quality of life. Regular monitoring of air quality and individual awareness of potential risks are paramount in minimizing long-term health consequences.
In conclusion, the impact of air pollution on respiratory wellness is a critical public health concern. Understanding the mechanisms, preventative measures, and treatment strategies is crucial for maintaining and improving public health. By adopting a holistic approach that incorporates individual responsibilities, governmental regulations, and scientific advancements, we can strive towards cleaner air and healthier respiratory systems for all. Take proactive steps to reduce your exposure to pollutants, support policies promoting clean air initiatives, and advocate for study and technological advancements in air quality management.